
1 hits
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) Analysis
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) analysis is a multi-physics study focusing on the interaction between fluids and solid structures, widely used in engineering, biomechanics, aerospace, and other fields. Below is a summary of its core content:
1. Basic Concepts
Coupling Mechanism: Fluids (liquids or gases) exert pressure, shear force, etc., on solid structures, causing structural deformation. In turn, structural deformation alters the flow field's boundary conditions, forming a two-way feedback loop.
Classification:
One-way coupling: The fluid affects the structure, but the impact of structural deformation on the flow field is negligible (e.g., wind loads on buildings).
Two-way coupling: Significant mutual influence between the fluid and the structure (e.g., heart valve movement, aircraft wing flutter).
2. Analysis Process
Modeling:
The fluid domain (governed by Navier-Stokes equations) and solid domain (governed by elastomechanics equations) are modeled separately.
Key parameters: Fluid viscosity, density; solid elastic modulus, Poisson's ratio, etc.
Mesh Generation:
Eulerian grids are typically used for the fluid domain, and Lagrangian grids for the solid domain.
Grid compatibility at the coupling interface must be ensured (e.g., Immersed Boundary Method, Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian method (ALE)).
Solution Methods:
Partitioned coupling: Fluid and solid are solved separately, with boundary data (e.g., force, displacement) exchanged through iteration.
Monolithic coupling: Directly solving coupled fluid and solid equations (highcomputational load but high accuracy).
Numerical Methods:
Finite Element Method (FEM) for solid analysis.
Finite Volume Method (FVM) or Finite Difference Method (FDM) for fluid analysis.
Coupling algorithms: Strong coupling (implicit), weak coupling (explicit).
3. Typical Application Scenarios
Aerospace: Wing flutter, rocket fuel tank sloshing.
Automotive engineering: Tire-water interaction, aerodynamic optimization.
Biomedical: Blood vessel wall and blood flow coupling, artificial heart valve design.
Energy engineering: Wind turbine blade vibration, nuclear reactor cooling systems.
4. Common Software
ANSYS Workbench: Integrates Fluent (CFD) and Mechanical (FEM), supporting two-way coupling.
COMSOL Multiphysics: Built-in FSI module, suitable for complex multi-physics problems.
ADINA: Specializes in strong-coupling FSI, applicable to large-deformation problems.
OpenFOAM: Open-source CFD tool, compatible with Code_Aster (FEM) for FSI analysis.

Figure 1: Cloud map of the wing's second-order modal shape
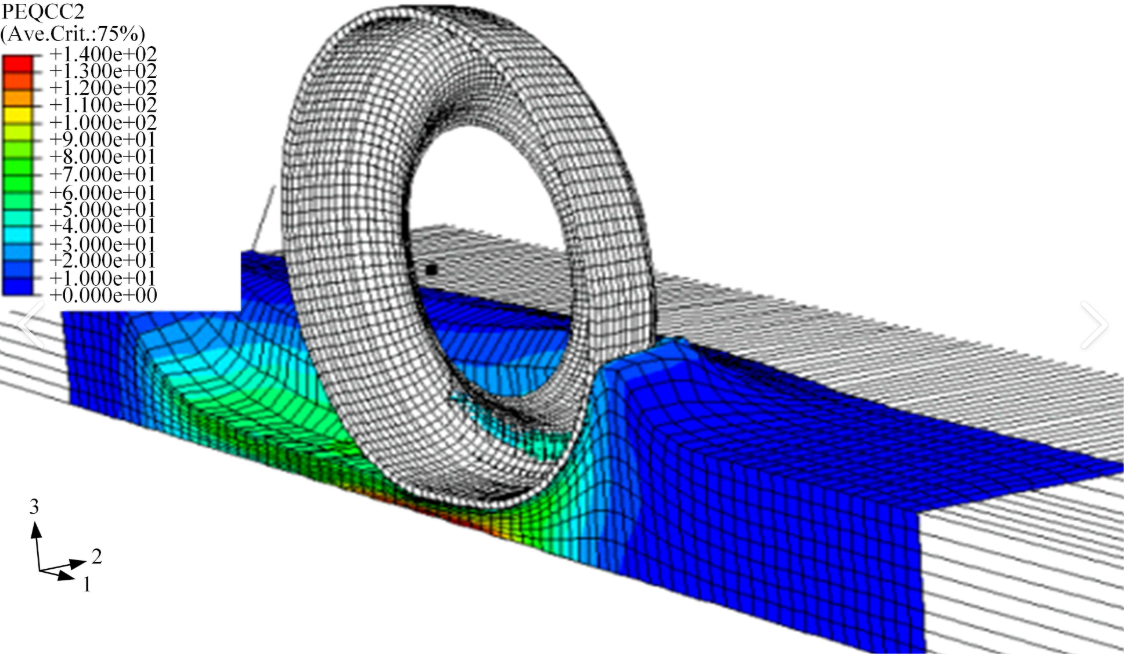
Figure 2: Tire-water flow interaction
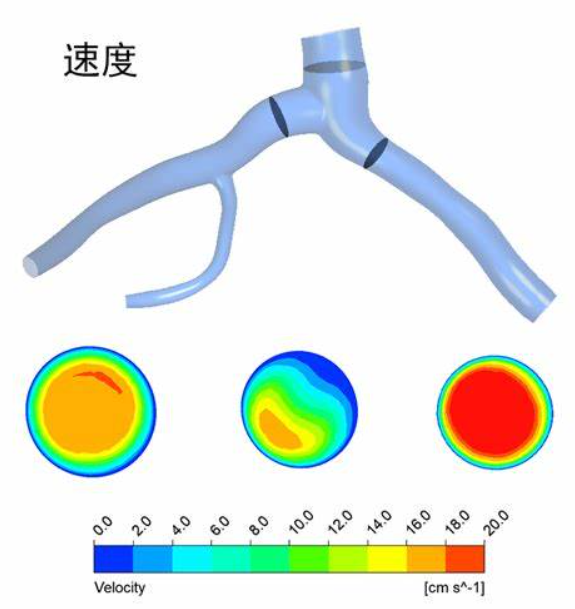
Figure 3: Coupling of blood vessel walls and blood flow
Contact:
Prof. Tian:WhatsApp:+86 15029941570 | Mailbox:540673737@qq.com
Copyright © 2025.Boye Engineering Technology All rights reserved. Yue ICP17017756Num-1