4 hits
2025/8/13 10:06:47
CAE Applications in Automotive Development
Generally, CAE is utilized across five key phases: conceptual design, detailed design, prototype, production, and improvement. As a computer-aided engineering tool, CAE is an integral part of this workflow. Design necessitates CAE support, manufactured products require physical testing for validation, forming a closed-loop cycle of "Design-CAE-Testing" in product development.

Traditional Automotive CAE Analyses are categorized into five computational types:
1.Stiffness & Strength Analysis
- Stiffness measures a structure's resistance to deformation under operational loads, focusing on permissible displacement. Simply put, good stiffness means minimal deformation.
- Strength evaluates a structure's load-bearing capacity, typically represented by peak stress. The key concern is whether stresses exceed material yield/ultimate limits—good strength means no failure.
- Often combined as "stiffness-strength" analysis since engineers monitor both macroscopic deformation and microscopic stress simultaneously.
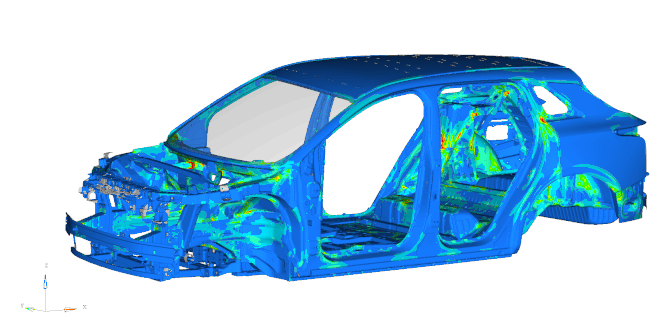
2.NVH Analysis (Noise, Vibration, Harshness)
Identifies modal parameters (frequency, mode shape, damping) via FEA to assess vibration/noise comfort under road/engine excitations. Effective NVH design enhances cabin smoothness and quietness. Key subsystems include:
- Body-in-white
- Engine/powertrain mounts
- Intake/exhaust systems
- Suspension-tire interactions
- Drivetrain
- Full-vehicle integration
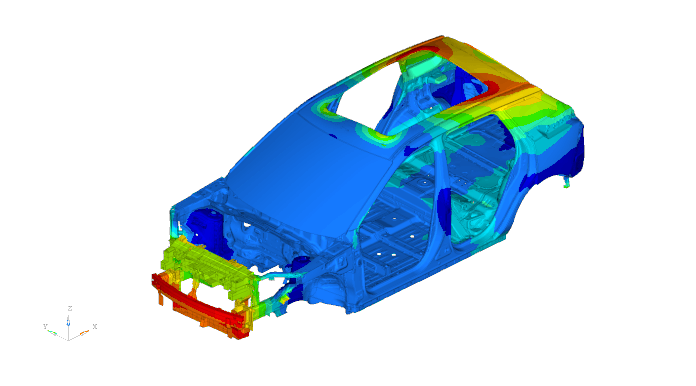
3.Fatigue & Durability Analysis
Predicts functional lifespan (measured in mileage) of critical components using:
- Road-load data acquisition
- Unit load stress/strain FEA calculations
- Material S-N curves
This reduces physical testing needs. Fatigue affects all mechanical systems, whether ICE or electric vehicles.
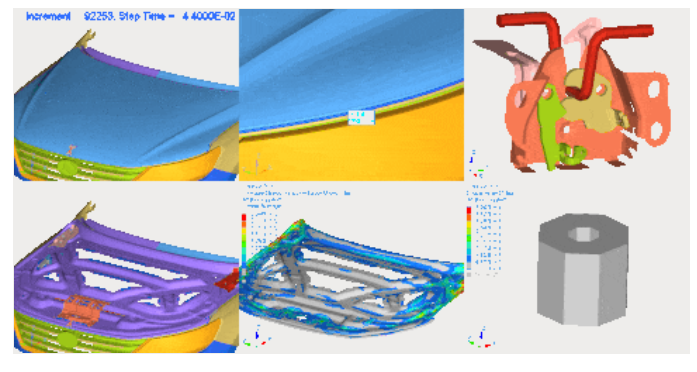
4.Crash Safety Analysis
Covers two domains:
- Active safety: Electronic controls (modeling/software testing)
- Passive safety: Structural crashworthiness, restraint systems (seatbelts/airbags), and occupant survival space optimization via CAE.
Global standards like C-NCAP (China's New Car Assessment Program) drive rigorous simulation requirements. CAE is now mandatory in vehicle development, with extensive benchmarking data enabling compliant safety structures.

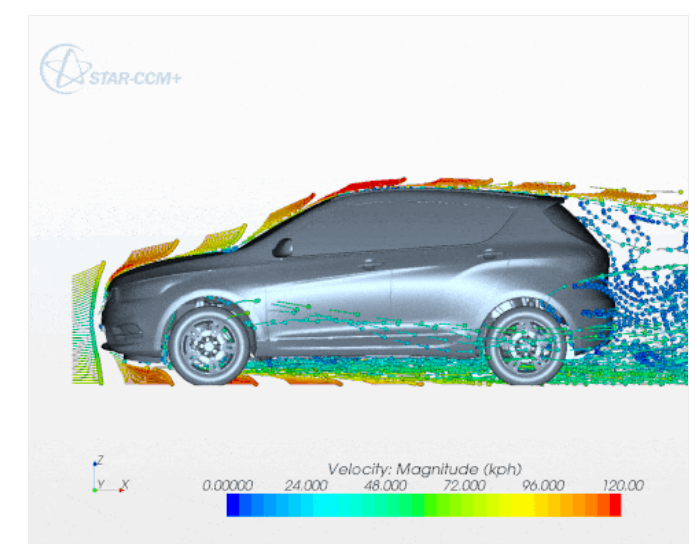
5.Fluid Dynamics Analysis (CFD)
Applications include:
- Exterior aerodynamics (drag reduction)
- Underhood cooling flow optimization
- Cabin thermal comfort/defrosting
- Engine combustion/emissions
- Cooling jacket/intake-exhaust flows
Aerodynamic design directly impacts styling, fuel economy, and wind noise—explaining the prevalence of streamlined shapes and active aero components.
Conclusion
This overview highlights five mature CAE domains in automotive engineering. Emerging frontiers include multidisciplinary co-simulation, multiphysics coupling, simulation process management, and automation. CAE remains a vast and evolving field.
Contact:
Prof. Tian:WhatsApp:+86 15029941570 | Mailbox:540673737@qq.com





